Pentacam®
For a High-Level Entry
The Pentacam® provides you with an overall view of the anterior eye segment in a matter of seconds. Measurements are performed by auto-release and are accompanied by a quality test, thus guaranteed to be fast, reproducible and delegable.
The Pentacam® comes with an extensive basic software package which can be extended according to your needs to include further optional software packages and modules.
Pentacam® Standard software
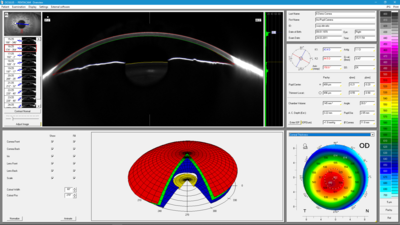
General Overview
Uses
- Comprehensive overview
- Patient consultation
Details
The General Overview provides important information on the keratometry and pachymetry of the cornea in concise numerical form. The Scheimpflug image provides ophthalmologists and their patients with intuitive representations of opacities of the cornea or lens (cataract) or of the position of existing IOLs. The anterior chamber is described in terms of anterior chamber depth, volume and angle. When combined with IOP tonometry readings corrected for corneal thickness the General Overview permits an assessment of glaucoma risk. It also allows the display of all color maps.
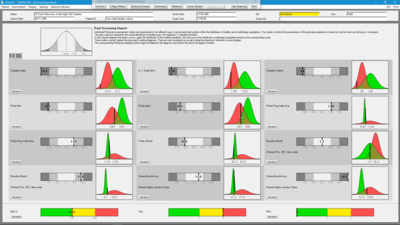
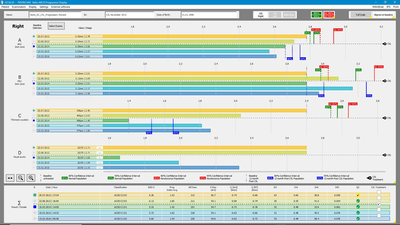
Fast Screening Report
Uses
- Quick detection of irregularities
- Patient consultation
Details
The Fast Screening Report provides an intuitive guide to review the Pentacam® results. It is a great tool for detecting abnormalities and to quickly screen new patients. Normative data is gathered from published studies and stored in the Pentacam® software. The distribution of normal values in a population is represented by the bars shaded in gray. The diagrams show the distribution for normal (green) and pathological (red) eyes. Sources, which the evaluations are based on, are cited to provide additional information. In cases of irregularities, the individual displays for detailed findings appear in the interactive navigation bar.
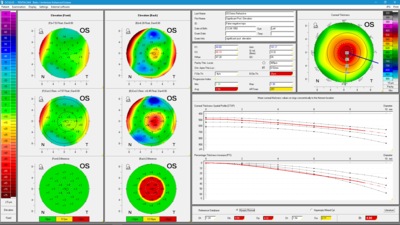
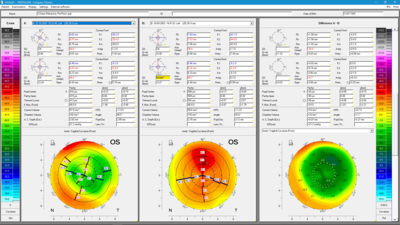
Belin/Ambrósio Display
Uses
- Evaluating the corneal shape
- Early detection of corneal changes
Details
The Belin/Ambrósio Display is the first screening tool to combine anterior and posterior corneal elevation data with an evaluation of corneal thickness progression in a final parameter, referred to as Index D. Besides allowing for greater overall accuracy in evaluating corneal abnormalities it can, in particular, assist in the early detection of these. It determines the progression of corneal thickness across an array of concentric rings centered on the thinnest point and reaching into the periphery. Two elevation maps are generated, one based on a standard reference surface and the other on an enhanced reference surface, and the differences found between them are shown in a color code to facilitate evaluation: green for unremarkable, yellow for conspicuous, and red for potentially pathological.
- Villavicencio et al, Independent Population Validation of the Belin/Ambrósio Display: Implications for KC Studies and Screening, Int. Journal of KC and Ectatic Corneal Diseases, Jan-Apr 2014;3(1):1-8
- Ambrosio et al; Corneal-thickness spatial profile and corneal-volume distribution: Tomographic indices to detect kc, J Cataract Refract Surg - VOL 32, NOVEMBER 2006
- Khachikian et al; Posterior Elevation in KC, Ophthalmology; Volume 116, Issue 4 , Pages 816-816.e1, April 2009
- Ambrosio et al; Corneal Ectasia After LASIK Despite Low Preoperative Risk: Tomographic and Biomechanical Findings in the Unoperated, Stable, Fellow Eye, J Refract Surg. 2010 Nov;26(11):906-11.
- Belin et al; Corneal Ectasia Risk Score: Statistical Validity and Clinical Relevance, Journal of Refractive Surgery Vol. 26, No. 4, 2010;
- Kim et al; Tomographic Normal Values for Corneal Elevation and Pachymetry in a Hyperopic Population, J Clinic Experiment Ophthalmol Volume 2, Issue 2, 1000130; ISSN:2155-9570;
- Feng et al; International values of corneal elevation in normal subjects by rotating Scheimpflug camera, J Cataract Refract Surg 2011; 37:1817-1821 Q 2011 ASCRS and ESCRS;
- Ambrosio et al; Novel Pachymetric Parameters Based on Corneal Tomography for Diagnosing KC, J Refract Surg. 2011 Oct;27(10):753-8;
- Correia et al; Topometric and Tomographic Indices for the Diagnosis of KC, International Journal of kc and Eczatic Diseases, May-August 2012; 1 (2):92-99;
- Gilani et al; Comprehensive anterior segment normal values generated by rotating Scheimpflug tomography, J Cataract Refract Surg 2013; 39:1707-1712 Q 2013 ASCRS and ESCRS;
- Ambrosio et al; Corneal Ectasia After LASIK Despite Low Preoperative Risk: Tomographic and Biomechanical Findings in the Unoperated, Stable, Fellow Eye, Journal of Refractive Surgery Vol. 26, No. 11, 2010
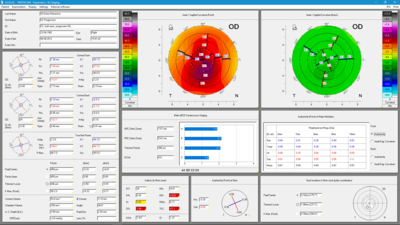
Topometric/KC-Staging
Uses
- Display of eccentricity results by zone
- Topography of the anterior and posterior corneal surface
Details
The rotating measurement principle guarantees high resolution output for the central cornea. The topographic analysis of the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces is based on the measured elevation data.
- Display of sagittal and tangential curvature of radius and refractive power
- Various elevation maps based on freely selectable reference surfaces
- Determination of true net corneal power with due consideration also to the posterior corneal surface
- Various four-map displays with default or freely configurable settings
- Subtractive and comparative representations of various examinations
Belin ABCD Progression Display
Uses
- KC progression for up to eight exams per eye
- Direct comparison of right and left eye
- Retrospective application
Details
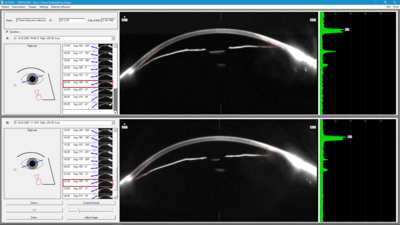
The Belin ABCD Progression Display allows direct comparison of up to eight exams per eye. The four parameters A (= anterior radius of curvature in 3 mm Zone), B (= back/posterior radius of curvature in 3 mm Zone), C (= corneal thickness at thinnest point) and D (= distance corrected visual acuity - DCVA) are displayed side by side to easily visually determine a trend of progression or depression (according to CXL). Each individual exam can be marked as baseline/reference (first exam by default) or as first exam after a cross-linking treatment (white/black bar line). The red and green lines describe the respective confidence intervals (CI). The red lines describe the group with kc, the green lines the normal/healthy group. The solid lines indicate the 95 % CI and the dashed lines the 80 % CI. The Belin ABCD KC Staging (Topometric/KC-Staging) and the Belin ABCD Progression Display can be used retrospectively.
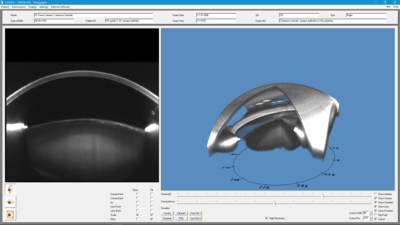
Tomography
Uses
- Changes which become visible in the Scheimpflug image are lucidly represented in a 3D model.
- Anterior segment tomography
Details
The rotatable, pivotable 3D model of the eye proves to be an enormous help when consulting with patients, as it permits the patient to see his or her eye from all sides so that irregularities can easily be explained. It provides a view of the anterior segment as a whole as well as separate views of the cornea and crystalline lens.
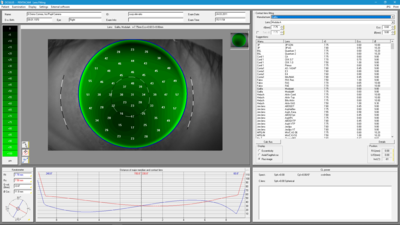
Contact Lens Fitting
Uses
- Automatic suggestions for contact lenses
- Realistic fluo image simulation
- Integrated database containing over 845,000 lenses
Details
Dynamic fluo image simulation produces an image of how a specific contact lens from the database fits on the eye. The simulation makes it possible to adjust the inclination and position of the contact lens and includes automatic recalculation of the fluo image. The integrated and expandable database contains over 845,000 lenses. The contact lens geometries can be adjusted individually in cases where fitting is difficult. The user can establish his or her own ranking list for contact lens manufacturers.
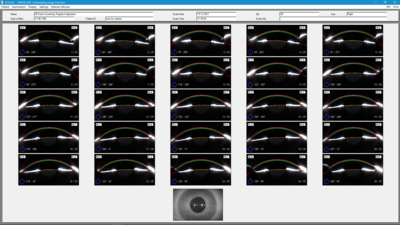
Scheimpflug Image Overview
Uses
- Check images for disruption due to blinking
- All Scheimpflug images at a glance
Details
All Scheimpflug images are shown. This makes it possible, for example, to spot interferences with the measurement process (light, blinking by the patient etc.) at a glance. This display appears directly after completion of the measurement, providing the option of stopping further calculations and repeating the measurement. However, this is not intended as an alternative to the automatic assessment of image quality, displayed as QS (quality specification).
The display is also useful for detecting first signs of opacification of the cornea or crystalline lens.